Ruby on Rails
Basics
Rails is a cool and expressive ruby framework aimed at web developement.
It is pragmatic in its philosophy, and thus uses an opinionated convention over configuration approach to developement.
Code looks nice and non bloated.
While not the most popular out there, ruby language has a strong community of developpers, making ruby packages available as "gems".
Requirements
Rails is a so-called ruby gem and needs to be installed with
$ gem install rails
A useful gem to install alongside is called bundler and allows dependencies bundling
$ gem install bundler
Kickstarting a rails app is as easy as running
$ rails new appname
This command creates a new folder called appname containing the application files
Using the bundler gem one can update and install gems specified in the file called Gemfile
$ bundle update && bundle install
Launching a server is achieved with
$ rails server -p $PORT -b $IP
Shortcuts
Rails conventions allows neat shortcuts
initialize database
rake is a gem equivalent to make but ruby flavored
$ rake db:create
launching a rails server
$ rails s
generating a new controller (Pascal case and plural)
$ rails g controller Pictures
One can add options to generate controller methods and associated routes and views
The following create the Pictures controller as well as index and show methods and associated routes
$ rails g controller Pictures index show
generating a model (Pascal singular)
$ rails g model Picture
One cand add options to generate a migration with table columns
The following creates a Picture model with a migration containing two fields: path of type string, and title of type text
$ rails g model Picture path:string title:text
Migrations are used to update db schema, pending migrations can be run with
$ rake db:migrate
To rollback the last migration (CAREFUL destructive operation ahead)
$ rake db:rollback
More in depth
Architecture
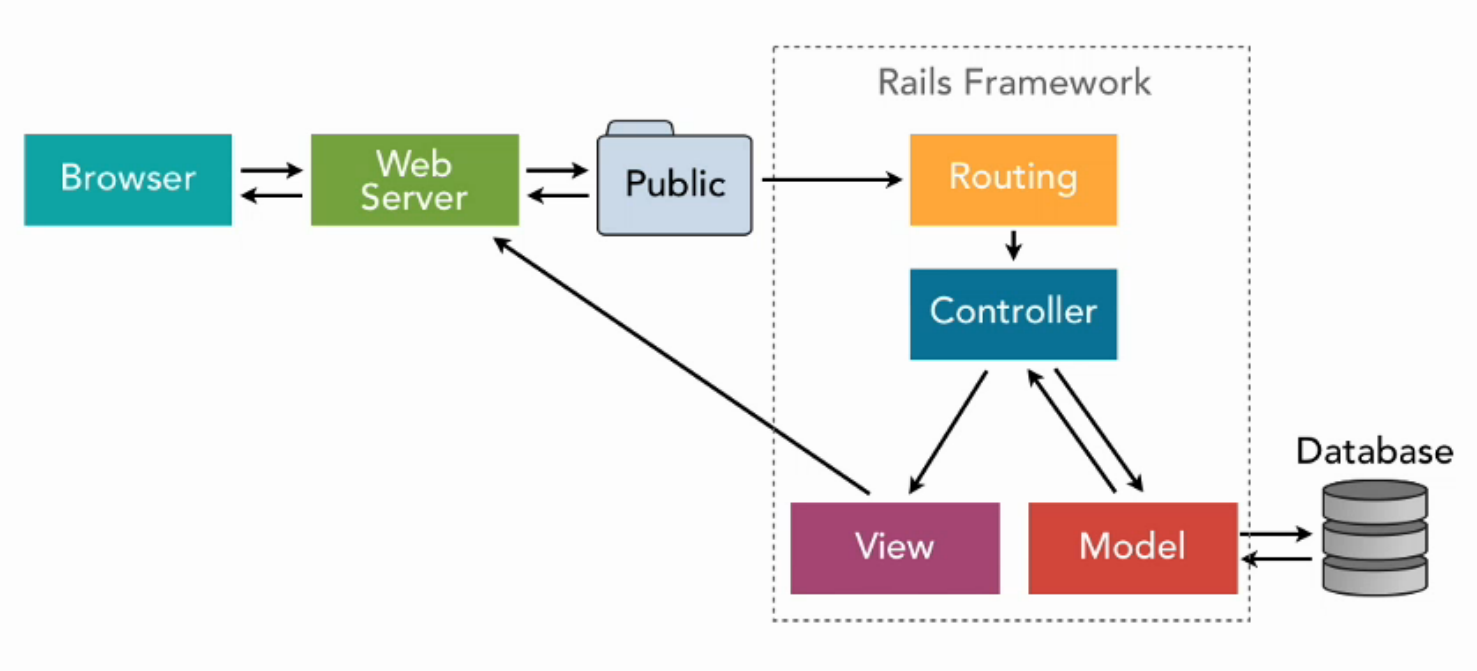
Create a new application
Install the Rails gem if you haven't done so before
$ gem install rails
Generate a new Rails app w/ Postgres support
$ rails new my_app --database=postgresql
Initialize the database
$ rake db:create
Start the Rails server
$ rails s
Routes
Create a route that maps a URL to the controller action
# config/routes.rb
get 'welcome' => 'pages#home'
Shorthand for connecting a route to a controller/action
# config/routes.rb
get 'photos/show'
# The above is the same as:
get 'photos/show', :to 'photos#show'
get 'photos/show' => 'photos#show'
Automagically create all the routes for a RESTful resource
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos

| HTTP Verb | Path | Controller#Action | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /photos | photos#index | display a list of all photos |
| GET | /photos_new | photos#new | return an HTML form for creating a new photo |
| POST | /photos | photos#create | create a new photo |
| GET | /photos/:id | photos#show | display a specific photo |
| GET | /photos/:id/edit | photos#edit | return an HTML form for editing a photo |
| PATCH/PUT | /photos/:id | photos#update | update a specific photo |
| DELETE | /photos/:id | photos#destroy | delete a specific photo |
Create resources for only certain actions
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos, :only => [:index]
# On the flip side, you can create a resource with exceptions
resources :photos, :except => [:new, :create, :edit, :update, :show, :destroy]
Create a route to a static view, without an action in the controller
# config/routes.rb
# If there's a file called 'about.html.erb' in 'app/views/photos', this file will be
# automatically rendered when you call localhost:3000/photos/about
get 'photos/about', to: 'photos#about'
Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/routing.html
Controllers
Generate a new controller
Note: Name controllers in Pascal case and pluralize
$ rails g controller Photos
Generate a new controller with default actions, routes and views
$ rails g controller Photos index show
Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/action_controller_overview.html
Models
Generate a model and create a migration for the table
Note: Name models in Pascal case and singular
$ rails g model Photo
Generate a model and create a migration with table columns
$ rails g model Photo path:string caption:text
The migration automatically created for the above command:
class CreatePhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration
def change
create_table :photos do |t|
t.string :path
t.text :caption
t.timestamps null: false
end
end
end
Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/active_model_basics.html
Migrations
Migration Data Types
:boolean:date:datetime:decimal:float:integer:primary_key:references:string:text:time:timestamp
When the name of the migration follows the format AddXXXToYYY followed by a list of columns, it will add those columns to the existing table
$ rails g migration AddDateTakenToPhotos date_taken:datetime
The above creates the following migration:
class AddDateTakenToPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
add_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
end
end
You can also add a new column to a table with an index
$ rails g migration AddDateTakenToPhotos date_taken:datetime:index
The above command generates the following migration:
class AddDateTakenToPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
add_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
add_index :photos, :date_taken
end
end
The opposite goes for migration names following the format: RemoveXXXFromYYY
$ rails g migration RemoveDateTakenFromPhotos date_taken:datetime
The above generates the following migration:
class RemoveDateTakenFromPhotos < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.0]
def change
remove_column :photos, :date_taken, :datetime
end
end
Scaffolding
Scaffolding is great for prototypes but don't rely too heavily on it: http://stackoverflow.com/a/25140503
$ rails g scaffold Photo path:string caption:text
$ rake db:migrate
Rake
View all the routes in an application
$ rake routes
Seed the database with sample data from db/seeds.rb
$ rake db:seed
Run any pending migrations
$ rake db:migrate
Rollback the last migration performed
NOTE: Be VERY careful with this command in production, it's destructive and you could potentially lose data. Make sure you absolutely understand what will happen when you run it
$ rake db:rollback
Path Helpers
Creating a path helper for a route
# Creating a path helper for a route
get '/photos/:id', to: 'photos#show', as: 'photo'
# app/controllers/photos_controller.rb
@photo = Photo.find(17)
# View for the action
<%= link_to 'Photo Record', photo_path(@photo) %>
Path helpers are automatically created when specifying a resource in config/routes.rb
# config/routes.rb
resources :photos
| HTTP Verb | Path | Controller#Action | Named Helper |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /photos | photos#index | photos_path |
| GET | /photos/new | photos#new | new_photo_path |
| POST | /photos | photos#create | photos_path |
| GET | /photos/:id | photos#show | photo_path(:id) |
| GET | /photos/:id/edit | photos#edit | edit_photo_path(:id) |
| PATCH/PUT | /photos/:id | photos#update | photo_path(:id) |
| DELETE | /photos/:id | photos#destroy | photo_path(:id) |
Asset Pipeline
Access images in the app/assets/images directory like this:
<%= image_tag "rails.png" %>
Within views, link to JavaScript and CSS assets
<%= stylesheet_link_tag "application" %>
<%= javascript_include_tag "application" %>
<!-- Filenames are fingerprinted for cache busting -->
<link href="/assets/application-4dd5b109ee3439da54f5bdfd78a80473.css" media="screen"
rel="stylesheet" />
<script src="/assets/application-908e25f4bf641868d8683022a5b62f54.js"></script>
Reference: http://guides.rubyonrails.org/asset_pipeline.html
Form Helpers
Bind a form to a model for creating/updating a resource
Use this method if you're using strong params to protect against mass assignment
# app/controllers/photos_controller.rb
def new
@photo = Photo.new
end
# ERB view
<%= form_for @photo, url: {action: "create"}, html: {class: "nifty_form"} do |f| %>
<%= f.text_field :path %>
<%= f.text_area :caption, size: "60x12" %>
<%= f.submit "Create" %>
<% end %>
<!-- HTML output -->
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/photos/create" method="post" class="nifty_form">
<input id="photos_path" name="photo[path]" type="text" />
<textarea id="photos_caption" name="photo[caption]" cols="60" rows="12"></textarea>
<input name="commit" type="submit" value="Create" />
</form>
Create a form with a custom action and method
<%= form_tag("/search", method: "get") do %>
<%= label_tag(:q, "Search for:") %>
<%= text_field_tag(:q) %>
<%= submit_tag("Search") %>
<% end %>
<form accept-charset="UTF-8" action="/search" method="get">
<input name="utf8" type="hidden" value="✓" />
<label for="q">Search for:</label>
<input id="q" name="q" type="text" />
<input name="commit" type="submit" value="Search" />
</form>